Understanding the Importance of Meal Timing for Diabetics
Myth Busting: Debunking Common Misconceptions About Diabetic Eating Habits
How often should a diabetic eat a day? This question often arises when managing diabetes. Meal timing plays a crucial role in diabetes management, impacting blood sugar levels and overall well-being. By understanding the importance of meal timing, individuals with diabetes can better control their condition and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Regular Meal Timing in Diabetes Management
Importance of Consistent Meal Schedule for Blood Sugar Control
Consistent meal timing plays a crucial role in managing diabetes effectively. When diabetics eat at regular intervals, it helps maintain stable blood glucose levels. Irregular eating patterns can cause fluctuations in blood sugar, leading to both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Therefore, understanding how often should a diabetic eat a day can significantly impact one’s health and well-being.
Impact of Skipping Meals on Blood Glucose Levels
Skipping meals can be particularly harmful for individuals with diabetes. When a meal is missed, the body may experience a drop in blood sugar levels, known as hypoglycemia. This can cause dizziness, confusion, or even fainting. On the other hand, the subsequent meal after a missed one may cause a spike in blood sugar. Hence, regular meals help keep blood sugar levels steady throughout the day.
Strategies for Creating a Balanced Meal Plan
Incorporating Whole Foods and Fiber for Sustained Energy
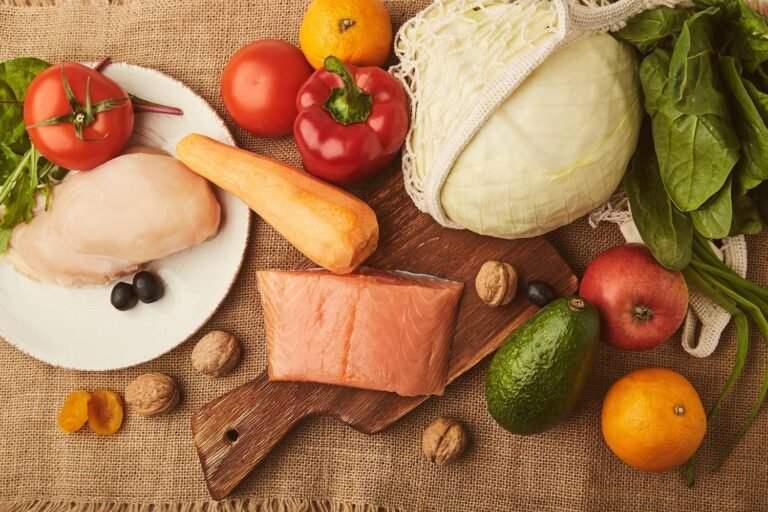
A balanced meal plan is essential for managing diabetes effectively. Incorporating whole foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes ensures a steady release of energy, preventing sharp spikes in blood glucose levels. Additionally, fiber-rich foods can improve digestion and support a healthy gut, which is particularly beneficial for diabetics.
- Vegetables: Kale, spinach, broccoli
- Fruits: Apples, berries, citrus fruits
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
Balancing Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats for Stable Blood Sugar
Balance is key to a diabetic-friendly diet. Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar, so it is essential to monitor their intake carefully. Combining carbohydrates with proteins and healthy fats can slow digestion and provide more sustained energy. For example, pairing a slice of whole-grain bread (carb) with avocado (fat) and chicken (protein) can make for a balanced meal.
Practical Tips for Establishing Healthy Eating Habits
Importance of Snacks in Managing Hunger and Blood Sugar Levels
Besides regular meals, healthy snacks can help manage hunger and maintain blood sugar levels throughout the day. Snacks should be nutrient-dense and low in sugars to avoid any unexpected spikes in glucose levels. Options like nuts, seeds, and yogurt can provide quick, healthy energy between meals.
Customizing Meal Frequency Based on Individual Needs and Lifestyle
The frequency of meals can vary from person to person. While some diabetics may benefit from eating small meals every three to four hours, others might find three main meals with a couple of snacks suitable. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine how often should a diabetic eat a day based on individual needs and lifestyle. Adapting meal times to fit daily routines can make managing diabetes more practical and sustainable.
- Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice
- Plan meals around daily activities and schedules
- Stay flexible and adjust meal times as needed
Closing Thoughts on Meal Frequency for Diabetics
When it comes to managing diabetes, paying attention to meal timing and frequency is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. By understanding the importance of consistent eating habits, individuals can better control their condition and improve their overall well-being. So, how often should a diabetic eat a day? While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, developing a personalized meal plan with the guidance of a healthcare provider can help determine the best approach for each individual’s unique needs.
Embracing a Balanced Approach to Eating
Remember that creating a balanced meal plan involves more than just counting calories or restricting certain food groups. It’s about nourishing your body with wholesome foods, incorporating a variety of nutrients, and finding a routine that works for you. Don’t forget the importance of regular snacks to help manage hunger and prevent blood sugar spikes. By prioritizing whole foods, fiber-rich options, and a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, you can support your overall health and diabetes care.
For more in-depth information on how meal frequency impacts diabetes care, check out our comprehensive guide on diabetes care.
Whether you need to eat three square meals a day or prefer smaller, more frequent snacks, the key is to listen to your body and work with your healthcare team to find a strategy that suits your lifestyle and health goals. By making mindful choices and staying informed about the latest recommendations, you can take proactive steps towards better managing your diabetes and promoting long-term well-being.