Aging and diet plan is crucial to apply when getting old. First, what is aging? This refers to the natural, gradual process of changes that occur in living organisms over time. It is a complex and multifaceted biological phenomenon that affects all living things, including humans. Aging encompasses various physical, physiological, and psychological changes that occur as an individual grows older. Here are some key aspects of aging:
- Biological Aging: This includes the physical changes that occur in the body over time. It involves processes like cell replication, DNA damage, and the gradual decline of various bodily systems and organs. Biological aging can lead to a decrease in physical strength, endurance, and overall functioning.
- Chronological Age: Chronological age is the number of years an individual has lived since birth. It is often used as a basic measure of how old a person is. However, it doesn’t necessarily reflect the overall health or functional abilities of an individual, as people of the same chronological age can experience aging differently.
- Physiological Changes: Aging can result in physiological changes such as a decrease in muscle mass, bone density, and skin elasticity. There may also be changes in hormone levels, metabolism, and immune system function.
While these are most of the aspects of aging that affect the everyday living of an individual:
- Cognitive Changes: Cognitive aging involves changes in mental abilities and cognitive functions. Common cognitive changes in aging may include slower information processing, decreased working memory, and changes in attention.
- Psychological Changes: Aging can bring about psychological changes, including shifts in priorities, goals, and emotional well-being. Older adults may experience changes in mood, such as increased happiness or contentment, but they may also be at greater risk for conditions like depression and anxiety.
- Social and Lifestyle Factors: Aging is influenced by various social and lifestyle factors, including nutrition, physical activity, access to healthcare, and social interactions. These factors can impact the rate and experience of aging.
- Longevity: Advances in healthcare and living conditions have contributed to increased life expectancy in many parts of the world. Longer lifespans have led to a growing aging population, which presents both opportunities and challenges for society.
It’s important to note that aging is a highly individualized process, and not all individuals age at the same rate or experience the same changes. Genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences can all play a role in how a person ages. Additionally, researchers continue to study the mechanisms of aging and explore ways to promote healthy aging and delay the onset of age-related diseases and conditions.
What is Diet Plan?
A diet plan is a structured and personalized approach to what and how you eat to achieve specific health and nutritional goals. Diet plans can vary widely depending on individual needs, preferences, and objectives. Here are some common elements and considerations when creating a diet plan:
- Determine Your Goals: Before creating a diet plan, identify your specific goals. These could include weight loss, muscle gain, improved athletic performance, managing a medical condition, or simply maintaining good health.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you have specific health concerns or conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian.
- Caloric Intake: Determine the appropriate daily caloric intake based on your goals. If you want to lose weight, you’ll typically need to consume fewer calories than you burn, while those looking to gain weight or maintain their current weight will need to match calorie intake with expenditure.
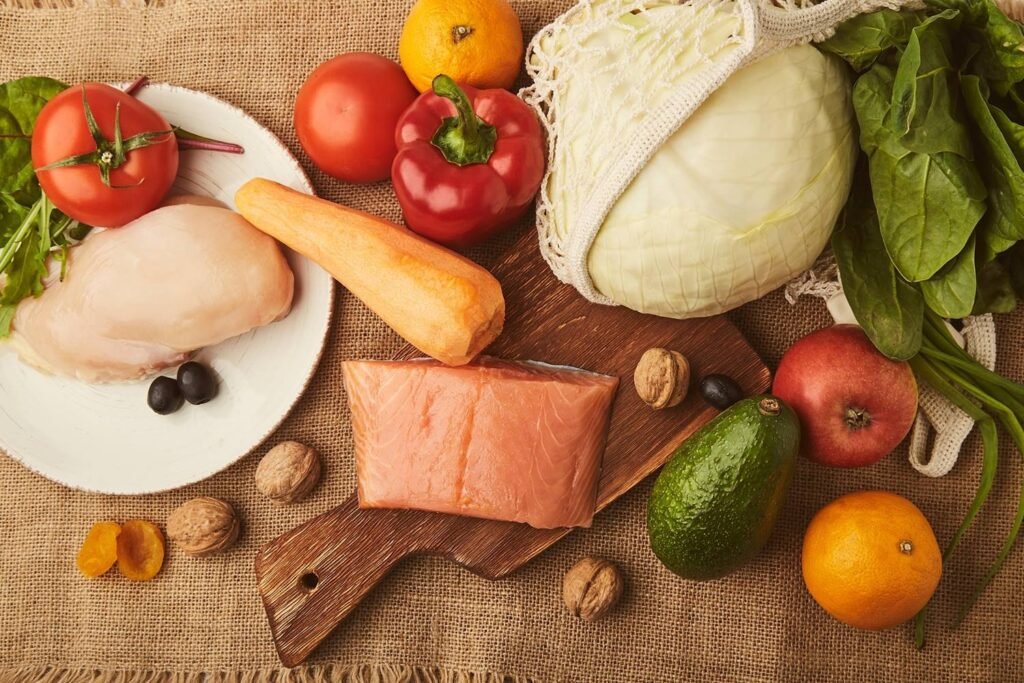
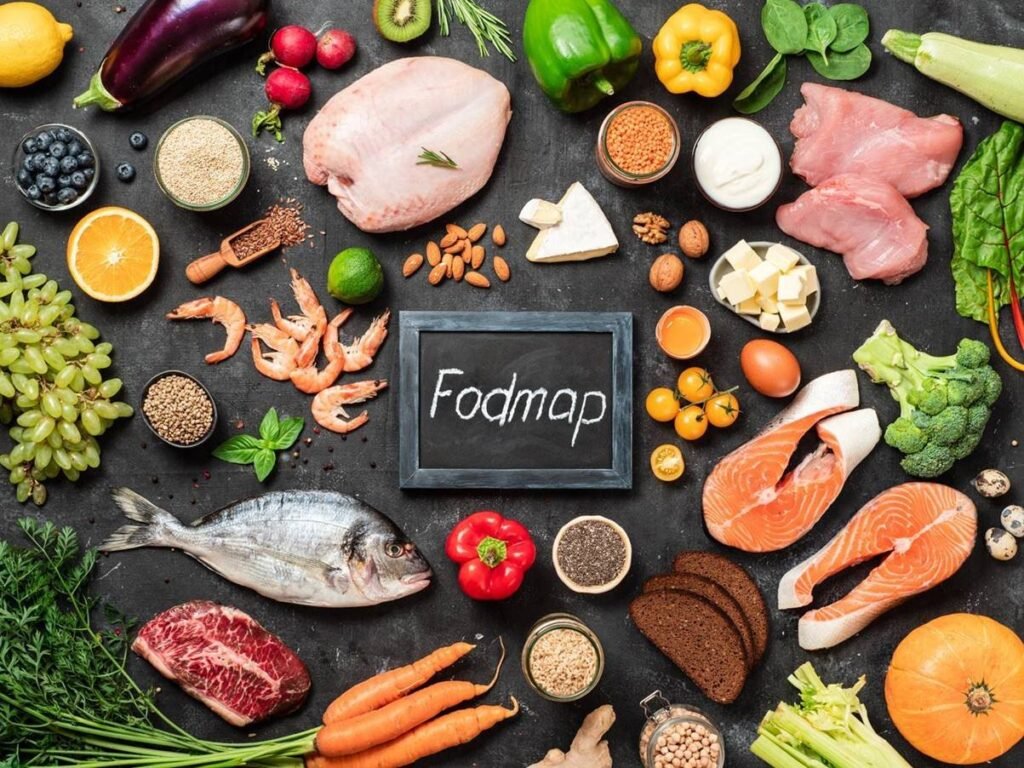
- Nutrient Balance: A well-rounded diet includes a balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). The specific balance may vary depending on your goals and dietary preferences. For example, a high-protein diet may be suitable for muscle building, while a low-carb diet might be chosen for weight loss.
Here are more tips on an effective diet plan when aging:
- Food Choices: Select a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods. Prioritize healthy fruits and minimize snacks that are not healthy such as sugary foods.
- Meal Planning: Create a daily or weekly meal plan that includes breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks. You can also plan for specific dietary requirements, such as vegetarian or gluten-free meals.
- Portion Control: Keep in mind your portion sizes to avoid undereating and overeating. This is crucial for weight management and calorie control.
- Hydration: Include an adequate intake of water in your diet. The amount needed varies from person to person, but staying hydrated is essential for overall health.
- Meal Timing: Some diet plans recommend specific meal timing strategies, such as intermittent fasting, while others prioritize regular, balanced meals throughout the day. Choose a timing pattern that suits your lifestyle and preferences.
- Lifestyle Factors: Consider how factors like physical activity, stress, sleep, and social interactions influence your dietary choices and overall health.
Remember that the best diet plan is one that is sustainable and aligns with your individual needs and goals. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition, so it’s essential to find a plan that works for you and promotes your long-term well-being. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian when making significant dietary changes.
What is a well balance diet plan while aging?
A well-balanced and healthy diet can have a significant impact on the aging process. Proper nutrition can support overall health, help maintain physical and cognitive function, and reduce the risk of age-related diseases and conditions. Here are some ways in which a diet plan can influence the aging process:
- Cellular Health: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help protect cells from oxidative stress and damage. This can slow down the aging of cells and may reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
- Muscle and Bone Health: Adequate protein intake, along with essential vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D, can help preserve muscle mass and bone density, which tend to decline with age.
- Heart Health: A diet low in saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars can lower the risk of heart disease and maintain cardiovascular health. Omega-3 fatty acids from sources like fatty fish can also support heart health.
- Cognitive Function: Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins, have been associated with better cognitive function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline in older adults.
- Gut Health: A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics can promote a healthy gut microbiome, which is linked to various aspects of health, including immune function and inflammation control.
Did you know that these may also affect your diet plan and aging?

- Inflammation Control: Chronic inflammation is associated with many age-related diseases. A diet that includes anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables can help reduce inflammation in the body.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet can reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and joint problems.
- Skin Health: Nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E, as well as antioxidants and healthy fats, can contribute to healthy skin, potentially reducing the signs of skin aging.
- Overall Well-Being: A balanced diet can provide the energy and nutrients needed for an active and fulfilling lifestyle in old age. It can also contribute to better mood and mental well-being.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the effects of diet on aging can vary from person to person and depend on individual factors like genetics, lifestyle choices, and overall health. Additionally, while a healthy diet is essential, it’s just one aspect of aging well. Other factors, such as physical activity, social connections, and stress management, also play crucial roles in healthy aging.
Ultimately, adopting a nutritious and balanced diet throughout life can contribute to a higher quality of life and promote successful aging. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian supports your unique needs and goals as you age.