Understanding Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. It often causes symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. Managing IBS involves understanding how certain foods can trigger or alleviate symptoms. By following a well-planned diet, individuals with IBS can find relief and improve their quality of life.
The Role of Diet in Managing IBS
Diet plays a crucial role in managing IBS symptoms. Certain foods can either worsen or alleviate symptoms, depending on the individual. By identifying trigger foods and incorporating gut-friendly options, individuals can effectively manage their IBS and promote gut health. Let’s explore the best foods to eat with IBS, foods to avoid, and tips for creating an IBS-friendly diet.
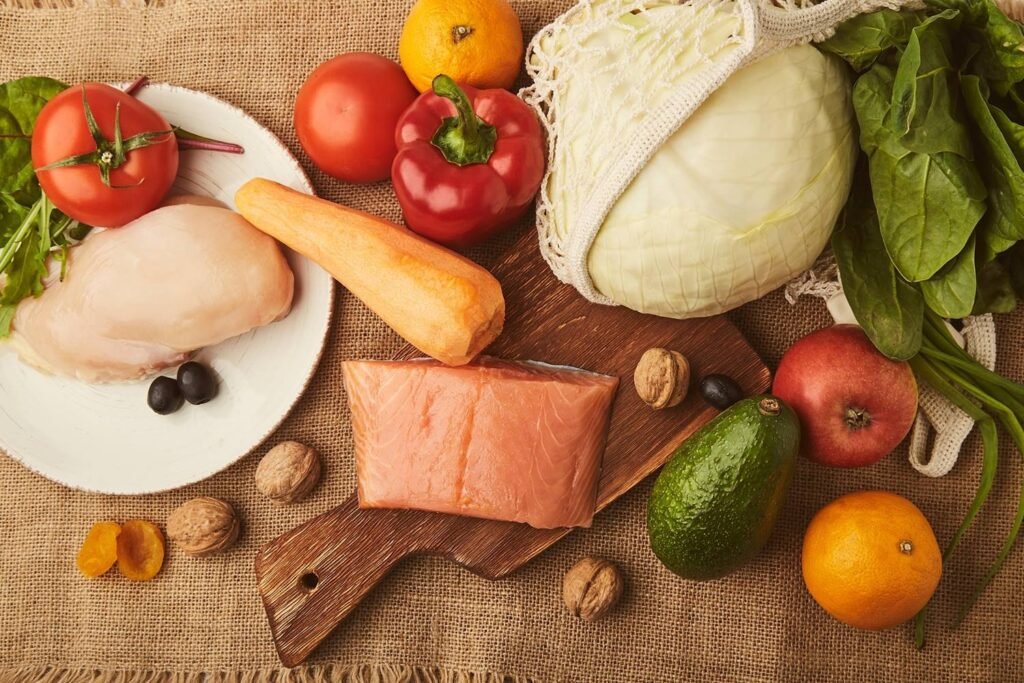
Best Foods for IBS Relief
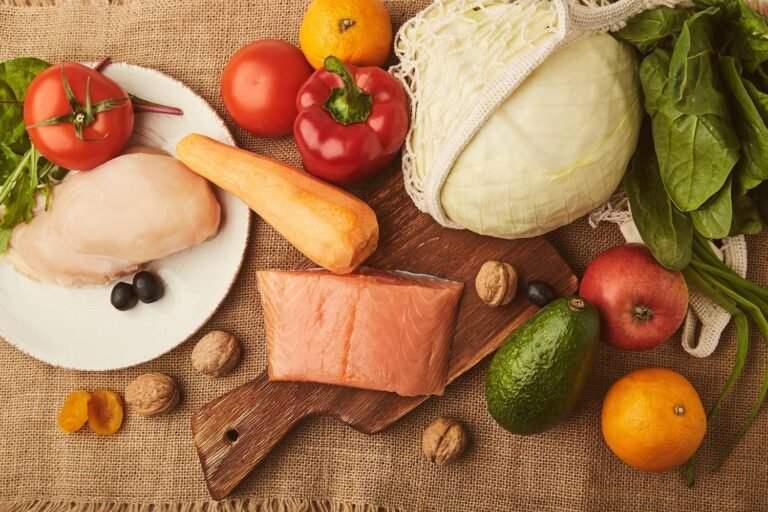
Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) with diet can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Including certain foods can help soothe the digestive system. Here are some of the best foods to eat with IBS:
- Low-FODMAP Foods: Foods low in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) are essential. Some examples include bananas, blueberries, cucumbers, and carrots.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, turkey, eggs, and fish are excellent protein sources that are gentle on the digestive system.
- Probiotic-rich Foods: Yogurt with live cultures, kefir, and sauerkraut can support gut health and reduce IBS symptoms.
- Soluble Fiber: Oats, apples, and carrots provide soluble fiber, which can help regulate digestion without causing bloating.
Foods to Avoid with IBS
While some foods can alleviate IBS symptoms, others can trigger or exacerbate them. Identifying and avoiding these common culprits can significantly help manage IBS:
- High-FODMAP Foods: Foods high in FODMAPs like onions, garlic, beans, and certain fruits such as apples and pears can trigger symptoms.
- Dairy Products: Lactose found in dairy can cause bloating, gas, and diarrhea in many individuals with IBS.
- Fried and Fatty Foods: Foods that are high in fat, such as fried items and fast food, can be difficult to digest, leading to more severe IBS symptoms.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Sweeteners such as sorbitol, often found in sugar-free gum and candies, can trigger digestive issues.
Tips for Creating an IBS-Friendly Diet
Planning and preparing meals thoughtfully can transform how one manages IBS daily. Applying these strategies can make a considerable difference:
Identify Your Triggers
Keeping a food diary is an effective method for tracking what you eat and identifying triggers. Recording your meals and symptoms can provide valuable insights into which foods you should avoid.
Engage in Mindful Eating
Eating smaller meals more frequently throughout the day can help reduce symptoms. Eating slowly and thoroughly chewing food can also aid in digestion and minimize discomfort.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is crucial for digestion and can help mitigate constipation, a common IBS symptom. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily to maintain optimal hydration.
Incorporate Fiber Gradually
While fiber is vital for digestive health, introducing it too quickly can cause bloating and gas. Gradually incorporating fiber into your diet allows your digestive system to adjust without undue discomfort.
Experiment with Cooking Methods
The way food is prepared can also impact IBS symptoms. Choosing baking, steaming, or grilling over frying can make meals easier to digest. Additionally, avoiding spicy seasonings can prevent irritation.
Final Thoughts on Managing IBS Through Diet
Creating an IBS-friendly diet can significantly impact your quality of life by managing symptoms and promoting gut health. By incorporating the best foods to eat with IBS and avoiding trigger foods, you can take control of your well-being.
Consistency is Key
Consistency in following an IBS-friendly diet is essential for long-term success. Make gradual changes to your eating habits and track how your body responds to different foods. Over time, you will discover what works best for your unique needs.
Seek Professional Guidance
If you are struggling to manage your IBS symptoms through diet alone, consider consulting a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian with experience in gastrointestinal health. They can provide personalized recommendations and support to help you navigate your dietary choices.
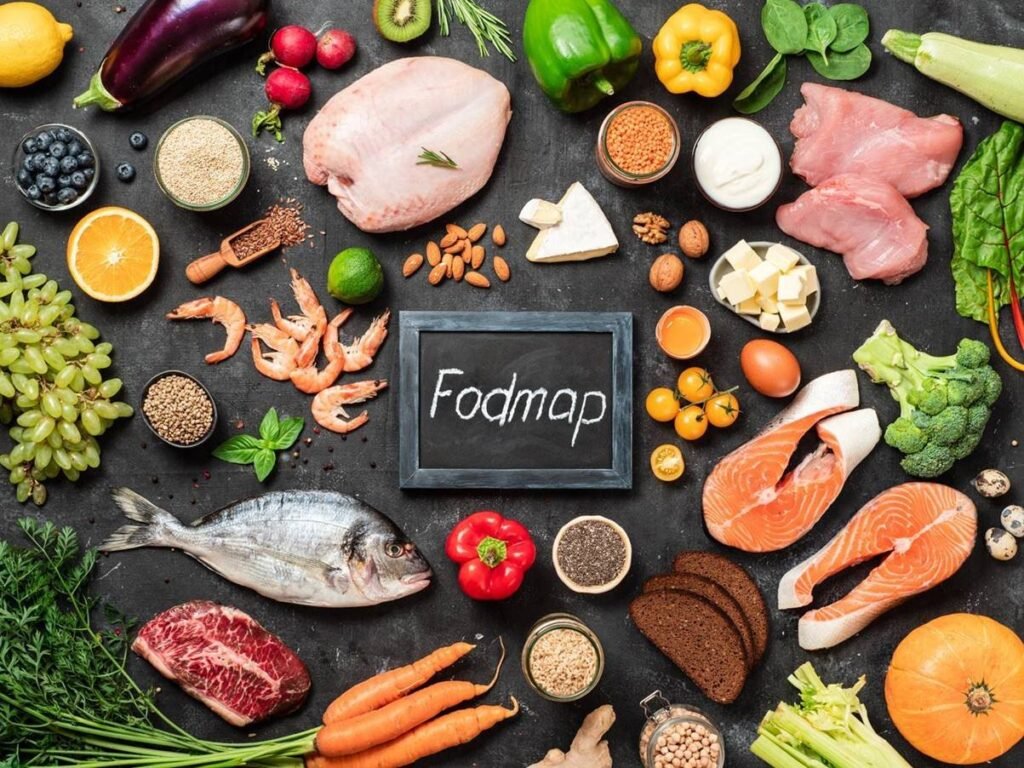
Exploring the FODMAP Approach
One popular dietary approach for managing IBS is the low FODMAP diet. FODMAPs are certain types of carbohydrates that can trigger digestive symptoms in some individuals. To learn more about FODMAPs and how this approach may benefit you, check out our article on FODMAP Diet.
Remember, managing IBS is a journey that requires patience and self-care. By arming yourself with knowledge about the best foods to eat with IBS and adopting healthy eating habits, you can proactively manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.