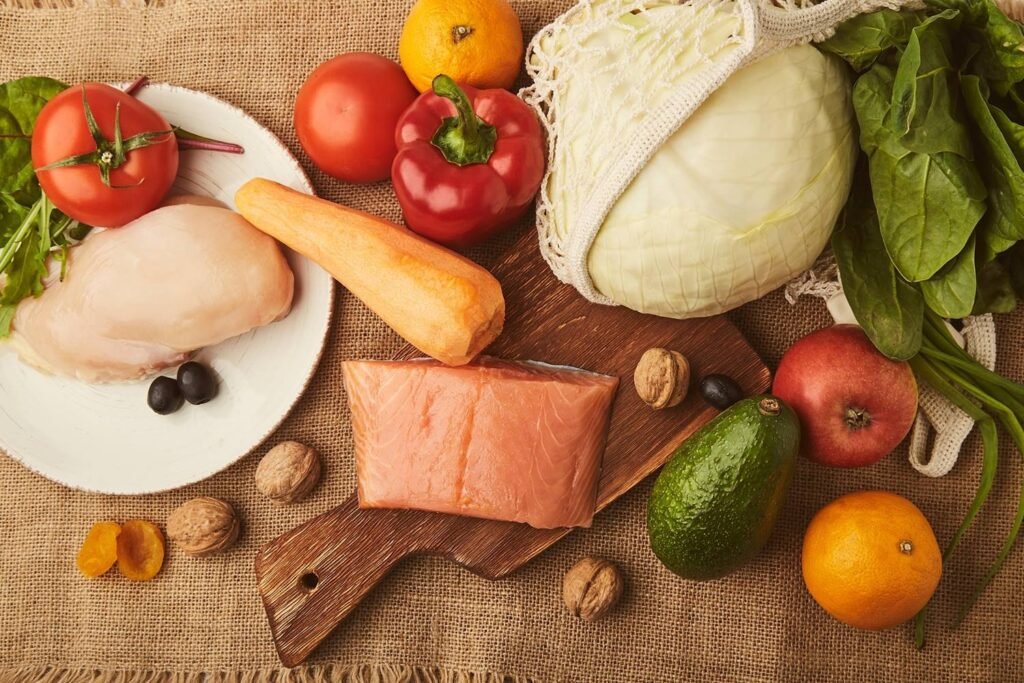
What we in take is important to consider especially for taking care of our health. This is why it is important to know food care for diabetes. Diabetes, often referred to as diabetes mellitus, is a chronic medical condition that affects how your body processes glucose (sugar), which is a primary source of energy for your cells. Glucose comes from the foods you eat and is carried by your bloodstream to cells throughout your body. To enter the cells and be used for energy, glucose requires a hormone called insulin.
Within the realm of metabolic mysteries, diabetes unveils its multifaceted nature through several distinct forms:
- Type 1 Diabetes: is like a story of the body’s immune system going rogue. Instead of protecting, it attacks and destroys important cells in the pancreas that make insulin. Without insulin, the body can’t control blood sugar properly. People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin injections for life to keep their blood sugar in check.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to the effects of insulin. It is often associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, and genetics. Type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood, but it is becoming increasingly common in younger individuals.
If not properly managed, high blood sugar levels can lead to various health complications over time, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, nerve damage, and more.
Common symptoms of diabetes can include:
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Weight loss (especially in type 1 diabetes)
- Blurred vision
- Slow wound healing
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet (due to nerve damage)
Diabetes management typically involves lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medication or insulin therapy. Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial to maintaining control. If you suspect you have diabetes or are at risk, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations. Proper management can help individuals with diabetes live a healthy and fulfilling life while reducing the risk of complications.
Diet Plan as Food Care for Diabetes
A diet plan is essential for managing diabetes because the foods you eat have a significant impact on your blood sugar levels. A well-designed diet plan for diabetes serves several critical purposes:

- Blood Sugar Control: The primary goal of a diabetes diet plan is to help you manage your blood sugar levels. By choosing the right types and amounts of foods, you can prevent spikes and drops in blood sugar, which is essential for avoiding complications and maintaining stable energy levels throughout the day.
- Carbohydrate Management: Carbohydrates are a key nutrient that has the most direct and immediate effect on blood sugar. A diabetes diet plan helps you monitor and control your carbohydrate intake. You can learn how to choose carbohydrates that have a smaller impact on blood sugar, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and how to balance them with insulin or medication.
- Weight Management: Many people with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese, and weight management is an important part of diabetes control. A diabetes diet plan can help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight, which can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Heart Health: A well-planned diet can help lower the risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels. This includes reducing saturated and trans fats and increasing the consumption of heart-healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Some of these tips may also help as food care for diabetes
- Energy Levels: Balancing your diet can help regulate your energy levels throughout the day. Consistent energy levels can improve your overall well-being and help you stay active, which is important for diabetes management.
- Preventing Complications: Proper nutrition can help prevent or manage complications associated with diabetes, such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems. A healthy diet can reduce the risk of these complications.
- Medication Management: In some cases, a well-planned diet can reduce the need for diabetes medications or insulin, or it can help individuals use these medications more effectively.
It’s important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all diet for diabetes. Diet plans should be tailored to individual needs, taking into account factors like age, activity level, weight, and any other health conditions. A registered dietitian or healthcare provider can help create a personalized diabetes diet plan that best suits your needs and helps you achieve and maintain good blood sugar control. Proper diet, when combined with medication or insulin as prescribed, can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Best Food Care for Diabetes
The “best” diet for diabetes can vary from person to person, depending on their specific needs, preferences, and medical conditions. However, some general dietary guidelines that are often recommended for people with diabetes include:

- Carbohydrate Management: Since carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, it’s crucial to monitor and control your carbohydrate intake.
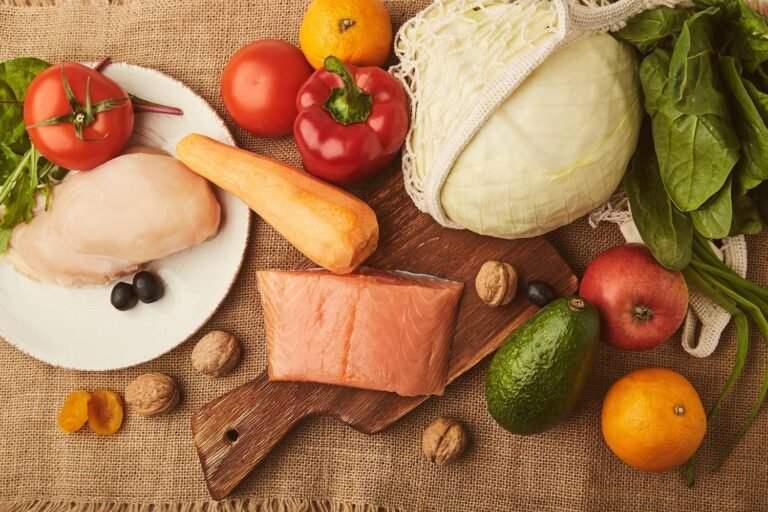
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote satiety.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources into your meals to help control hunger and maintain muscle mass. Good options include skinless poultry, lean cuts of meat, fish, tofu, tempeh, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats: Choose heart-healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel).
- Portion Control: Use measuring cups and a food scale if needed. Eating consistent portions can help manage blood sugar levels.
In addition, meal timing and planning is important. These are more tips about food care diabetes:
- Regular Meal Timing: Try to eat at regular intervals throughout the day to help stabilize blood sugar levels. Skipping meals can lead to erratic blood sugar fluctuations.
- Limit Added Sugars: Minimize or eliminate foods and beverages with added sugars, such as sugary drinks, candies, and desserts. Opt for sugar-free or reduced-sugar alternatives when possible.
- Meal Planning: Consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that suits your needs and preferences.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as recommended by your dietician.
Remember that it’s crucial to individualize your diet plan to meet your specific goals and dietary preferences.
Conclusion
Diabetes management may involve medication or insulin therapy. A registered dietitian with expertise in diabetes can provide tailored recommendations to help you achieve blood sugar control.
Get to know more about tips for healthy aging: