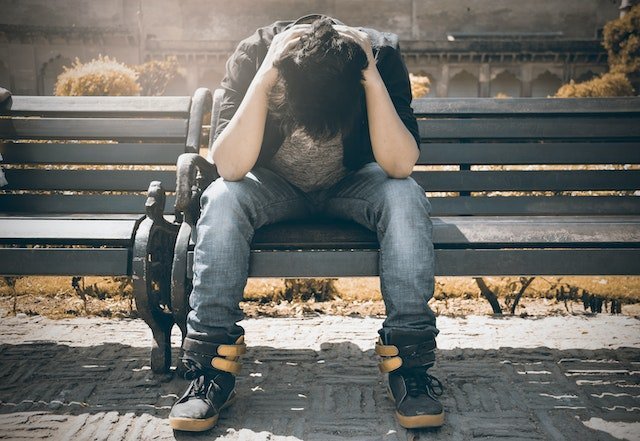
Bipolar depression, often referred to as bipolar disorder or manic depression, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings or episodes of mania and depression. It is a complex disorder that affects a person’s mood, energy levels, and ability to function in daily life. This blog will give you more insight about the signs of Bipolar Depression.
There are several key features of bipolar depression:
- Manic Episodes: Individuals with bipolar disorder experience manic episodes, which are periods of intense and elevated mood. During a manic episode, a person may feel extremely happy, have high energy levels, engage in impulsive behaviors, and have a decreased need for sleep. Manic episodes can be so severe that they lead to significant impairment in daily functioning.
- Depressive Episodes: Bipolar depression involves episodes of deep and persistent sadness, low energy, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyed. These depressive episodes can be similar to major depressive disorder and may include symptoms like changes in appetite and sleep patterns, feelings of worthlessness, and difficulty concentrating.
- Cycling: The hallmark of bipolar disorder is the cycling between manic and depressive episodes. Some individuals may experience rapid cycling, with frequent mood swings within a short period, while others have less frequent episodes. There can also be periods of relative stability between episodes.
- Types of Bipolar Disorder: Varieties of Bipolar Disorder may manifest on the following
- Bipolar I Disorder: defined by experiencing at least one manic episode, potentially followed by depressive episodes.
- Bipolar II Disorder: Involves at least one major depressive episode and one hypomanic episode (a less severe form of mania).
- Cyclothymic Disorder: Marked by chronic mood disturbances, with periods of hypomanic symptoms and depressive symptoms that do not meet the criteria for a full manic or major depressive episode.
In case symptoms got worst, these are things you must consider:
- Treatment: Bipolar disorder is typically managed with a combination of medication (mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, antidepressants) and psychotherapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or psychoeducation). Lifestyle modifications, including regular sleep patterns, stress management, and avoiding substance abuse, are also important components of treatment.
It’s important to note that bipolar disorder is a lifelong condition, but with appropriate treatment and support, many individuals with the disorder can lead fulfilling and stable lives. Diagnosis and treatment should be provided by mental health professionals who can tailor their approach to the specific needs of each individual. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of bipolar depression, it is important to seek help from a healthcare provider.
Signs of Bipolar Depression
Bipolar depression, a component of bipolar disorder, is characterized by episodes of depressive symptoms alternating with episodes of mania or hypomania (elevated mood and increased activity). The signs and symptoms of bipolar depression can vary in severity and duration but typically include the following:
- Persistent Sadness: Individuals with bipolar depression often experience deep and persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and emptiness. This emotional state can last for an extended period.
- Loss of Interest: A loss of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable, including hobbies, social interactions, and work, is common during depressive episodes.
- Fatigue and Low Energy: People with bipolar depression frequently feel extremely tired, lacking the energy to carry out daily tasks. This fatigue may be physically and mentally draining.
- Sleep Disturbances: Sleep patterns can be disrupted, leading to either insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep) or hypersomnia (excessive sleep).
- Changes in Appetite and Weight: Changes in appetite may occur, resulting in either overeating and weight gain or loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Feelings of Worthlessness or Guilt: Individuals with bipolar depression may experience intense feelings of worthlessness, guilt, or self-criticism.
Other signs of Bipolar Depression that is pertinent to individuals are:
- Difficulty Concentrating: Concentration and focus may become challenging during depressive episodes, making it difficult to perform tasks that require attention.
- Physical Symptoms: Some people with bipolar depression may also experience physical symptoms such as aches, pains, and digestive problems.
- Social Withdrawal: Depressive episodes can lead to social withdrawal and isolation, as individuals may find it difficult to engage with others.

It’s important to note that the severity and duration of depressive symptoms can vary among individuals with bipolar disorder. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of bipolar depression, it is crucial to seek help from a mental health professional. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference in managing bipolar disorder and improving quality of life.
How to Deal with Bipolar Depression?
Dealing with bipolar depression can be challenging, but there are effective strategies and treatments available to help manage the condition and improve your overall well-being. Here are some steps to consider:
- Consult a Mental Health Professional: The first and most crucial step is to seek professional help. A psychiatrist or a mental health counselor with experience in bipolar disorder can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
- Medication: Medications, including mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, are commonly prescribed to manage bipolar depression. It’s essential to take your medications as prescribed and communicate any side effects or concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Therapy: Psychotherapy or talk therapy can be an essential component of treatment. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT) can help you learn to manage depressive symptoms, identify triggers, and develop coping strategies.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making positive changes in your lifestyle can have a significant impact on managing bipolar depression. Consider the following:
- Regular Sleep Patterns: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, as disruptions in sleep can trigger mood swings.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption.
- Avoid Substance Abuse: Alcohol and recreational drugs can worsen bipolar symptoms, so it’s essential to avoid them.
Other ways to deal with bipolar depression that you must need to know:
- Support System: Build a strong support network of family and friends who can offer understanding and encouragement. Consider joining a support group for individuals with bipolar disorder to connect with others who share similar experiences.
- Recognize Early Warning Signs: Learn to recognize the early signs of mood changes, whether they are depressive or manic, so you can seek help or adjust your treatment plan promptly.
- Create a Crisis Plan: Share this plan with a trusted person in your support network.
- Stay Informed: Educate yourself about bipolar disorder and its treatment options. Understanding the condition can help you make informed decisions about your treatment and self-care.
- Monitor Your Mood: Keep a mood diary to track your mood fluctuations, sleep patterns, and any potential triggers.
- Follow-Up Care: Keep up with mental health professional check-ins to track progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Addressing bipolar depression is a continual journey, and discovering the optimal treatment combination may require patience. Be patient with yourself and reach out for help and support when needed. Bipolar disorder is a treatable condition, and with proper management, many individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
Explore more – Bipolar Disorder Therapies